
Publications
Our publications are intended to help inform important public health issues in our state and region. Please feel free to contact us with thoughts and quesitons as you have opportunity to review our work.

The rise in e-cigarette use among youth has been a growing public health concern since 2015, peaking in 2019. Although usage rates have since declined, they remain high, with 10% of high school and 4.6% of middle school students reporting use in 2023. This report highlights the implementation and evaluation of the CATCH My Breath e-cigarette prevention program in eight central Appalachian counties, an area with some of the nation's highest tobacco use and poor health outcomes.
The program, conducted between 2019 and 2023, reached over 6,200 students across 25 schools in West Virginia and Kentucky. The impact of the program was assessed through pre- and post-test surveys, measuring students' knowledge of e-cigarettes and their current use. Results demonstrated a significant improvement in knowledge and beliefs, as well as reductions in current use and peer influence on e-cigarette use.
The success of CMB in these counties has supported the expansion of the program to all 55 West Virginia counties in collaboration with the West Virginia Department of Health.
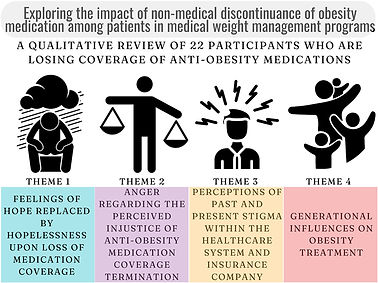
This study investigates the impact of insurance discontinuation of anti-obesity medications on patients in a West Virginia medical weight management program. It finds that losing coverage led to feelings of hopelessness, anger, and stigma, highlighting the importance of continued access to these medications for effective obesity treatment and overall health. Participants expressed concerns about weight regain and the negative effects on mental health and family well-being. The study calls for better policy and communication regarding insurance coverage for obesity treatments.

The study investigates the impact of transportation, Medicaid-funded non-emergency medical transportation (NEMT), and telehealth on access to medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for opioid use disorder (OUD) in rural West Virginia. Survey results from 225 individuals reveal transportation as a critical factor in both initiating and sustaining treatment, with NEMT services proving unreliable for many. While telehealth offers an alternative, challenges persist, highlighting the importance of tailored approaches to treatment access and the necessity for diverse care options to support individuals with OUD in their recovery journey.

Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is a life-saving intervention for opioid use disorder (OUD). Despite its proven benefits, only a small percentage of eligible individuals in the United States access MAT, and retention remains a challenge. This study explores factors influencing entry and sustained participation in MAT, emphasizing insights from individuals in recovery. The findings contribute valuable insights to enhance care delivery and support those undergoing treatment.

Opioid addiction and opioid-related overdoses and deaths are serious public health problems nationally and in West Virginia, in particular. Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is an effective yet underutilized treatment for opioid use disorder. This research examines factors that help individuals succeed in MAT from the perspective of those in recovery.
This study aimed to estimate the availability of food, supplies, and medicine, areas of greatest concern, the most acceptable and effective methods of communication, and the need for acute intervention for older adults aged 75 years or older and living in rural central Appalachia during the COVID-19 pandemic. In this population, systematically telephoning rural elderly patients during the COVID-19 epidemic and its aftermath represents an effective strategy for providers who care for elderly rural patients.


Work related burnout is highly prevalent in US physicians and linked to adverse effects on patients, providers and organizations. This study measures burnout in West Virginia primary care providers, allowing for comparison of results to a similar, recent study of US physicians.

This study highlights the need for further exploration into the fidelity of PHQ-2 delivery and acceptance of a pre-recorded tablet-based delivery of the PHQ-2 among patients and health care providers.

This research provides primary care practices with a refined decision support tool for evaluating the fit of research opportunities for their unique practices.